
Advanced freeform polyurethane foam dressing in aluminised polyethene packaging. The dressing is obtained by mixing two components: polyol (with the addition of nanocrystalline boehmite) and isocyanate. When applied to the wound, the foam mass forms a fine-pored elastic coating of 0.8–1.0cm thickness. The dressing is designed to maintain a moisture-rich environment to provide optimal conditions for wound healing, while managing exudate and reducing the risk of infection. It is intended to promote faster recovery and increased comfort, reducing recovery time, costs and the risk of complications associated with traditional dressings.



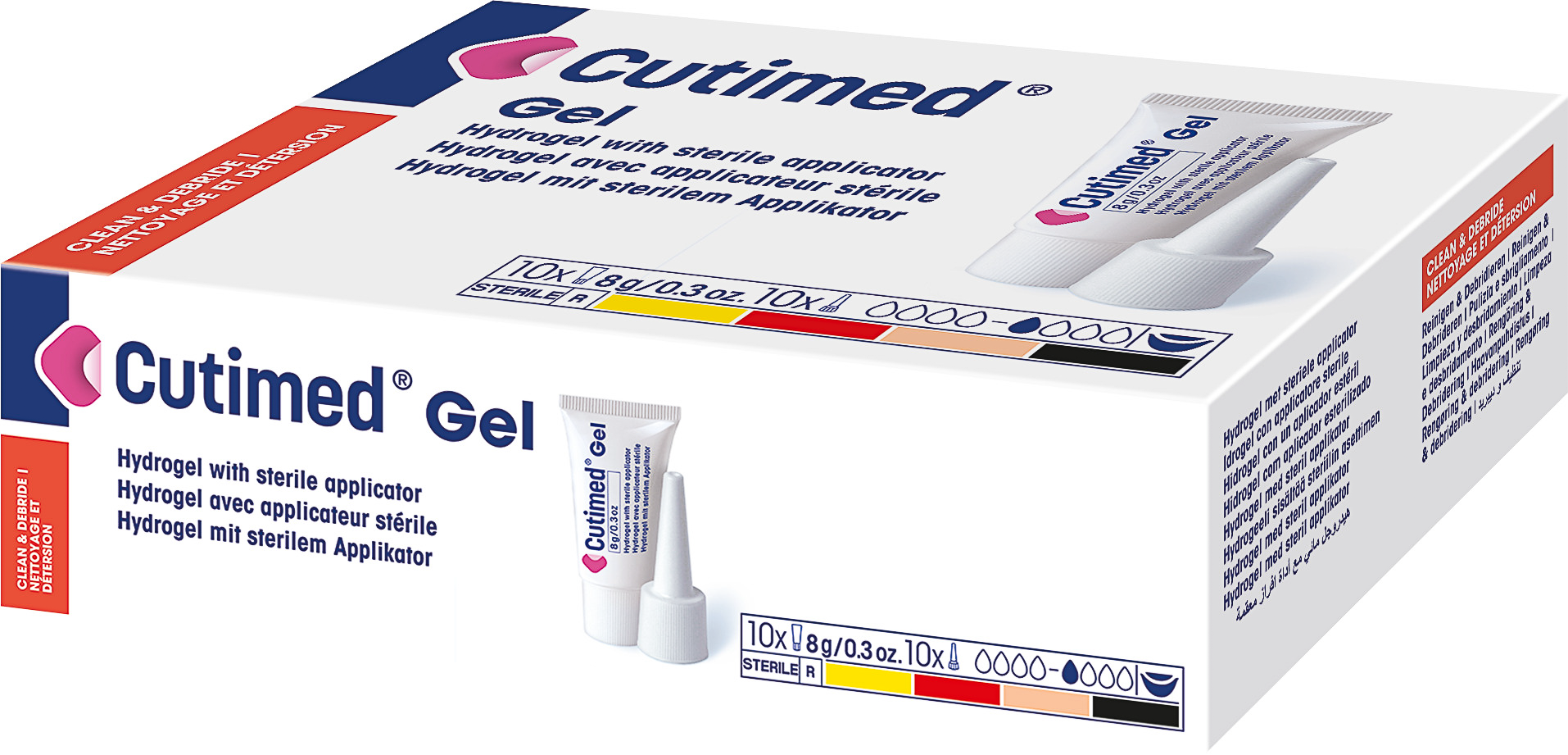
A transparent, amorphous hydrogel. It supports a moist wound environment and thereby contributes to autolytic wound cleansing.
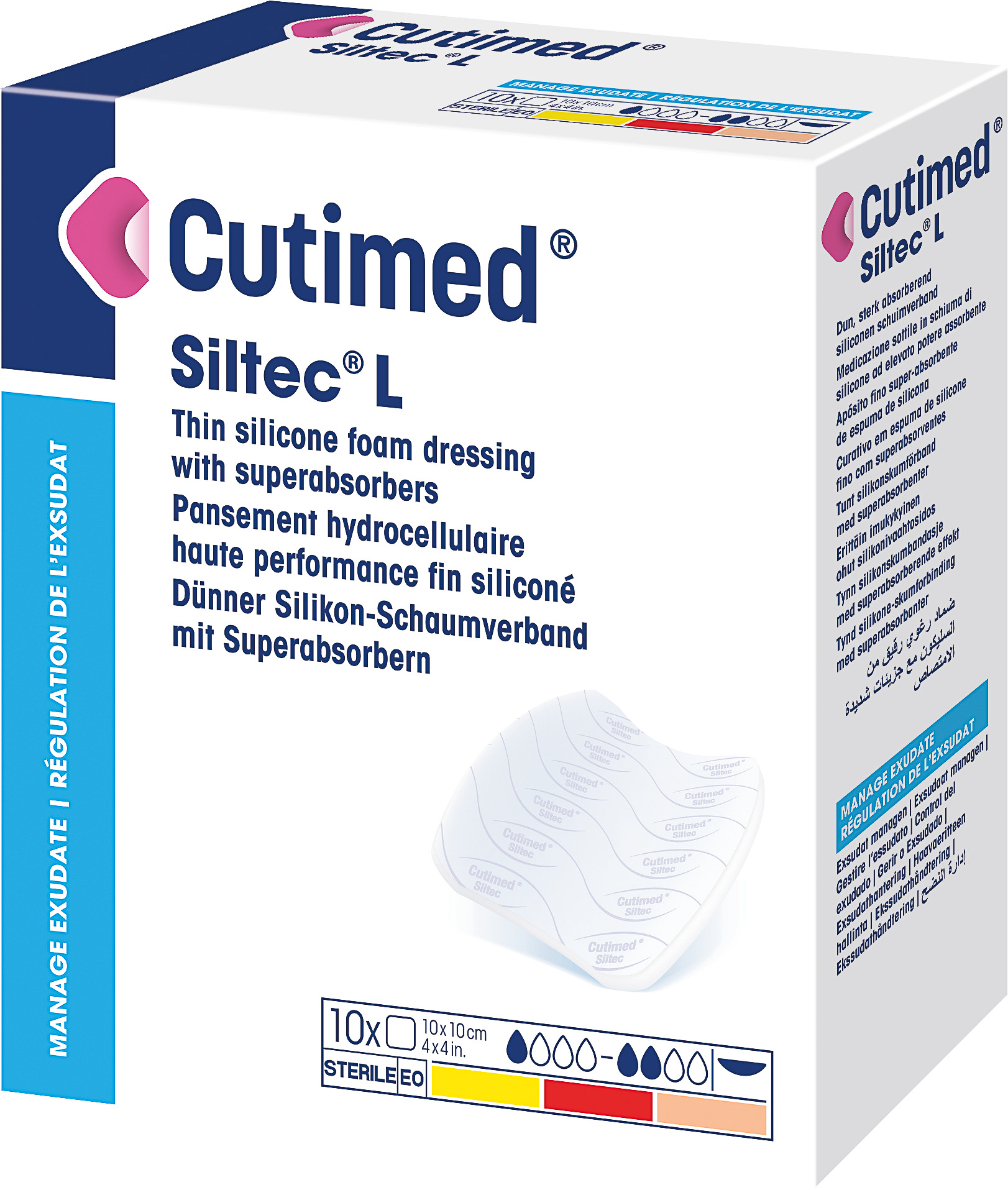
A thin silicone foam dressing for atraumatic dressing changes that contains superabsorbent stripes which absorb and lock wound exudate.

Pro-ionic hydrogel contact layer and fluid-repellent, polyurethane film outer layer. Available in non-adhesive and adhesive options.

Synthetic dermal scaffold that provides an effective reconstructive option for a range of complex wounds. The Biodegradable Temporising Matrix (BTM) enables the generation of a vascularised neodermis, which provides a more robust foundation for wound reconstruction than grafting alone, limiting wound scarring and contracture.
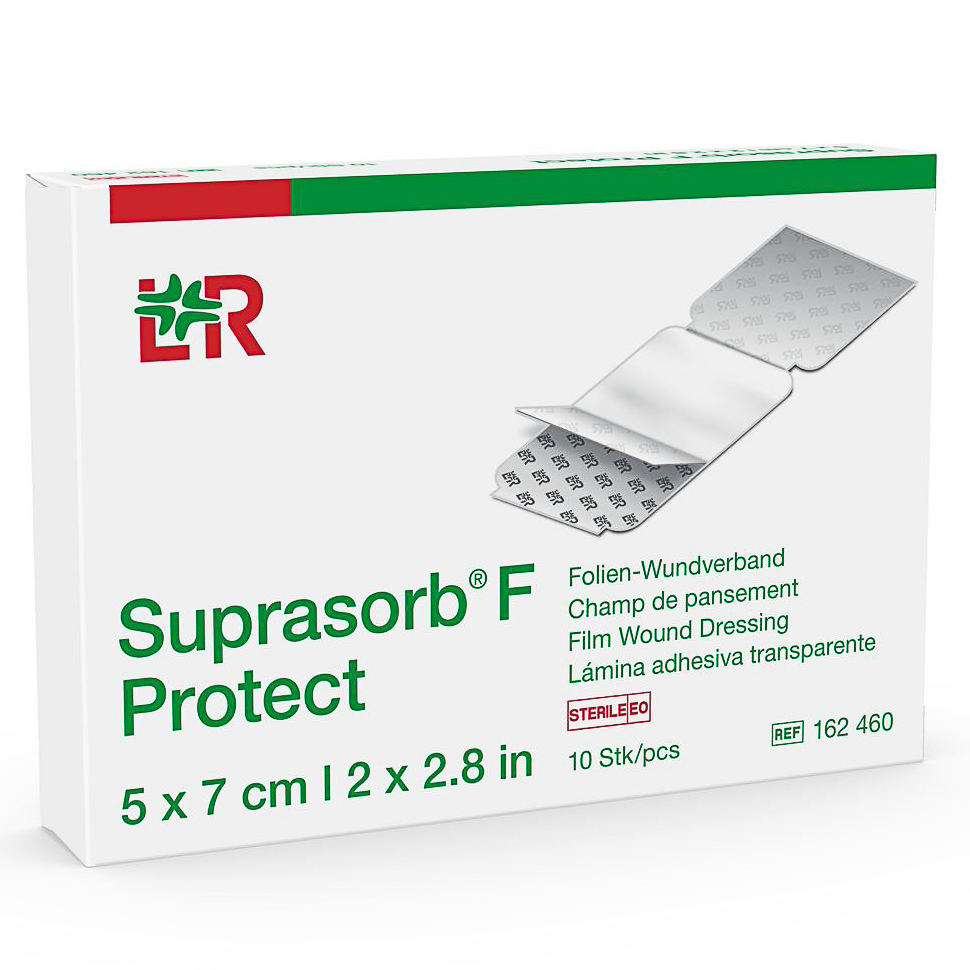
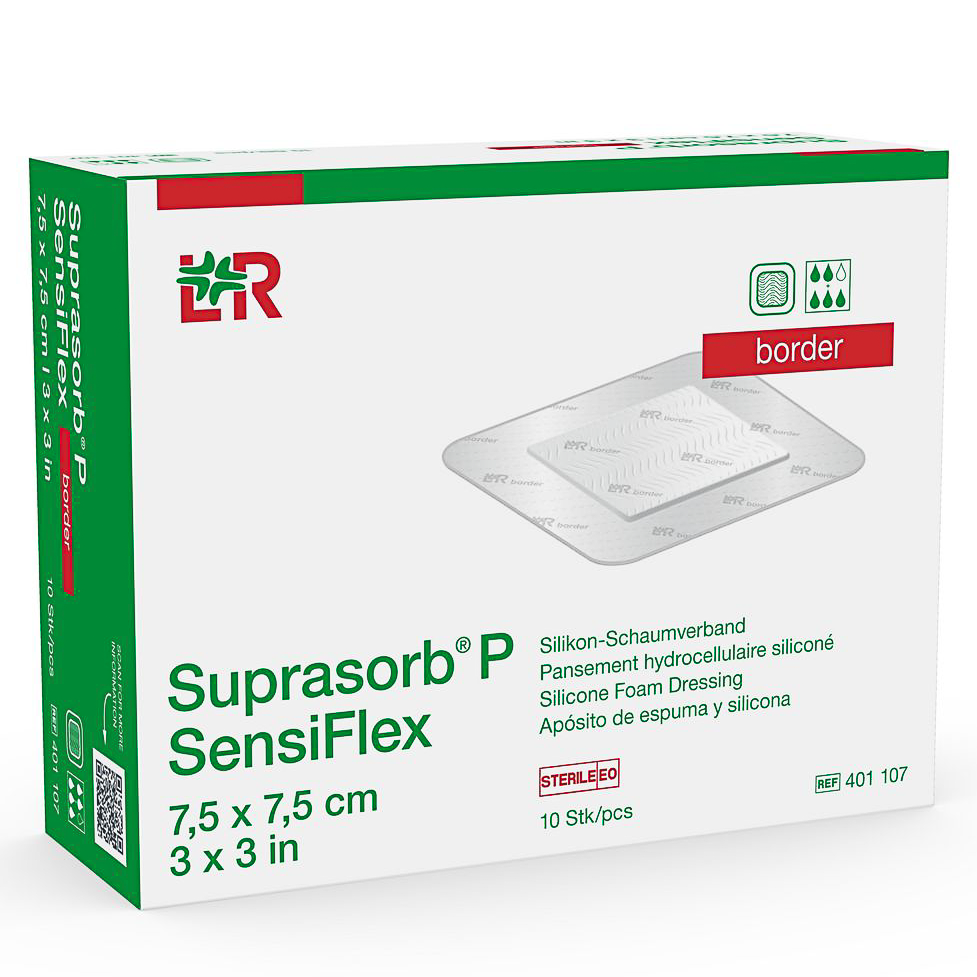
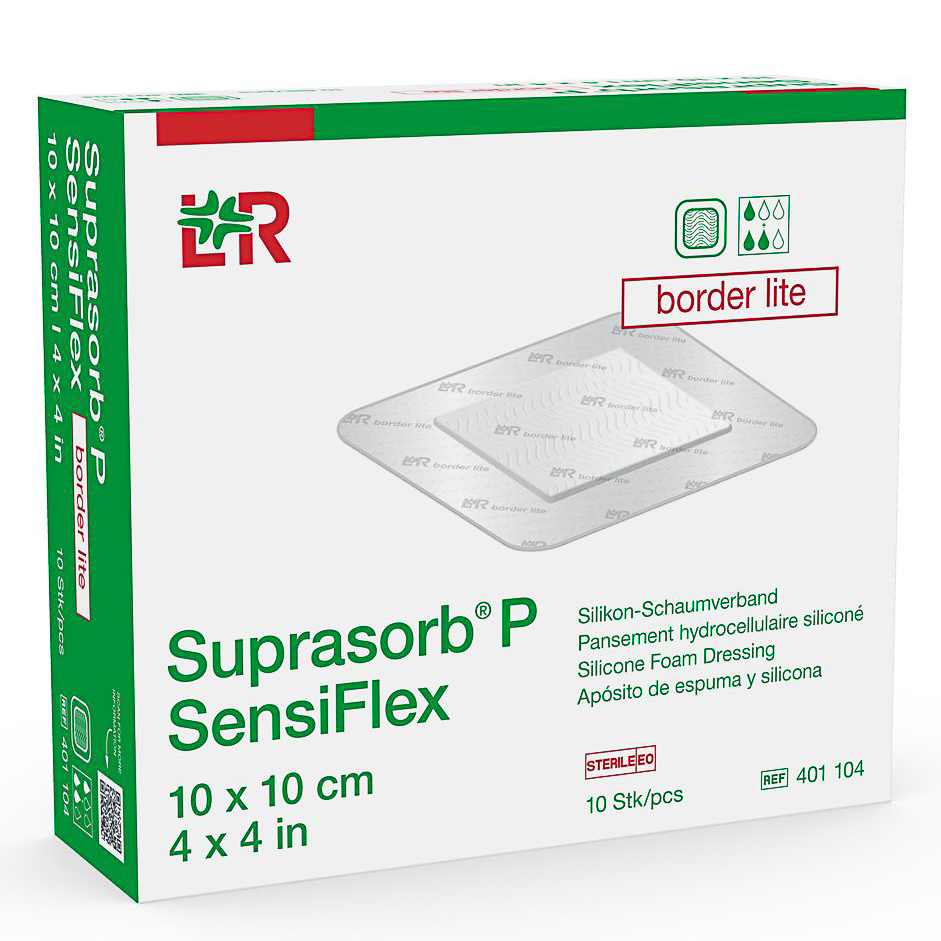






Flexible lipido-colloid non-occlusive contact layer containing TLC-NOSF healing matrix that jellifies in contact with wound exudate, reducing MMP levels and restoring balance to close wounds sooner, regardless of wound type.